1. Timeline of protocols date of birth and development
Ever since the invention of Guglielmo Marconi’s monopole antenna in 1895 people have been fascinated by the possibilities of communicating wirelessly. Even in the present day, with all the wireless communication we have around us, we still project this fascination out into our future—think about the ComBadges featured in Star Trek: The Next Generation as just one pop culture example.
Beginning in the mid-20th Century, wireless communication innovation has been picking up speed, from short-range RFID in the late 1940s to the incredible data rates we enjoy today through modern Wi-Fi.
To help you keep track of these innovations, we’ve prepared historical timelines of each wireless technology that give an overview of each technology’s evolution and what companies have backed-up and/or are using the protocol.
1.1 Overview of communication protocols evolution
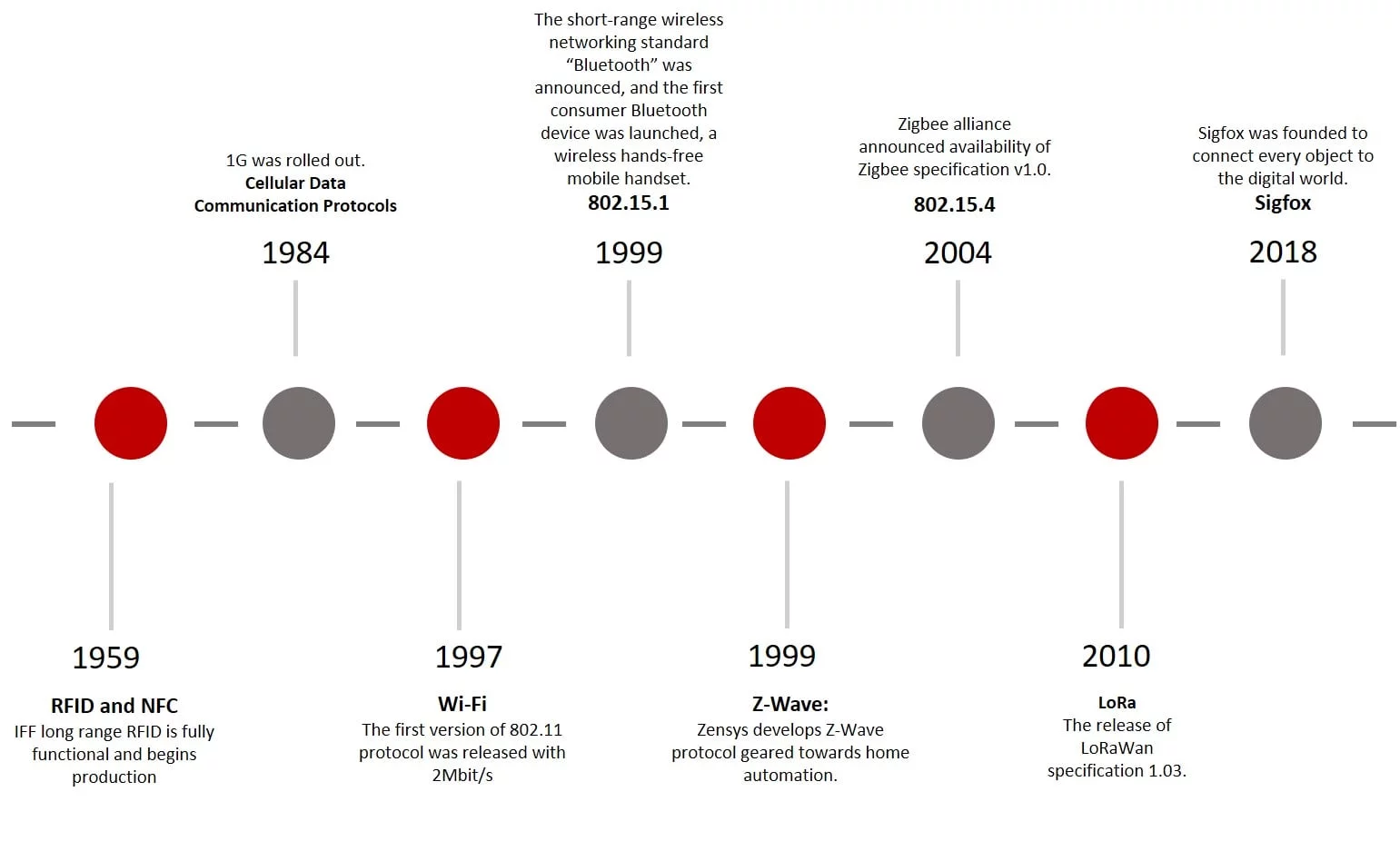 Figure 1 - Overview of communication protocols evolution
Figure 1 - Overview of communication protocols evolution
IEEE 802.11 - Wi-Fi Wireless Local Area Network
Wi-Fi was created to allow household and office devices and equipment to wirelessly connect and interface with the internet.
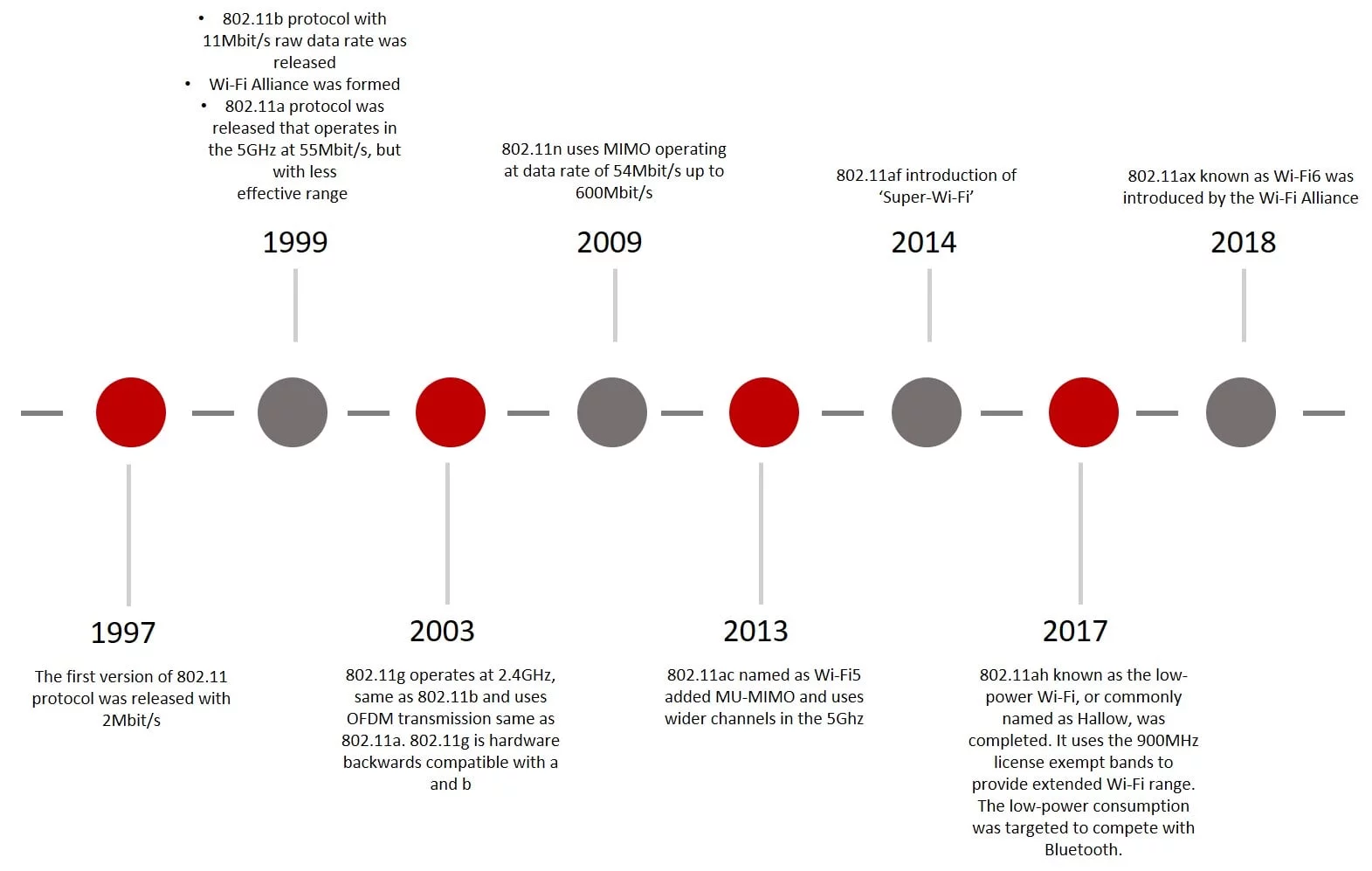 Figure 2 - Wi-fi evolution
Figure 2 - Wi-fi evolution
More Info…
To better improve indoor Wi-Fi performance please visit: Home Wi-Fi Improvement Guide
IEEE 802.15- Wireless Personal Area Networks
802.15 standard was created to interconnect personal electronic devices
1997: Fedex and other companies are looking for a standard suitable for devices typically worn
1999: 802.15 was formed to deal with Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN)
2002: 802.15.1 aka Bluetooth was published
2003: 802.15.4 LR-WPAN (Low Rate WPAN) was released
Sources – for more information please visit:
http://ieee802.org/15/index.html
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IEEE_802.15
IEEE 802.15.1 – WPAN/ Bluetooth
802.15.1 was introduced to allow the exchange of data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances using short-wavelength UHF radio waves in the industrial, scientific and medical radio bands. These wireless protocols operate in the unlicensed RF frequency bands (2402 -2483.5 MHz worldwide) since 2003.
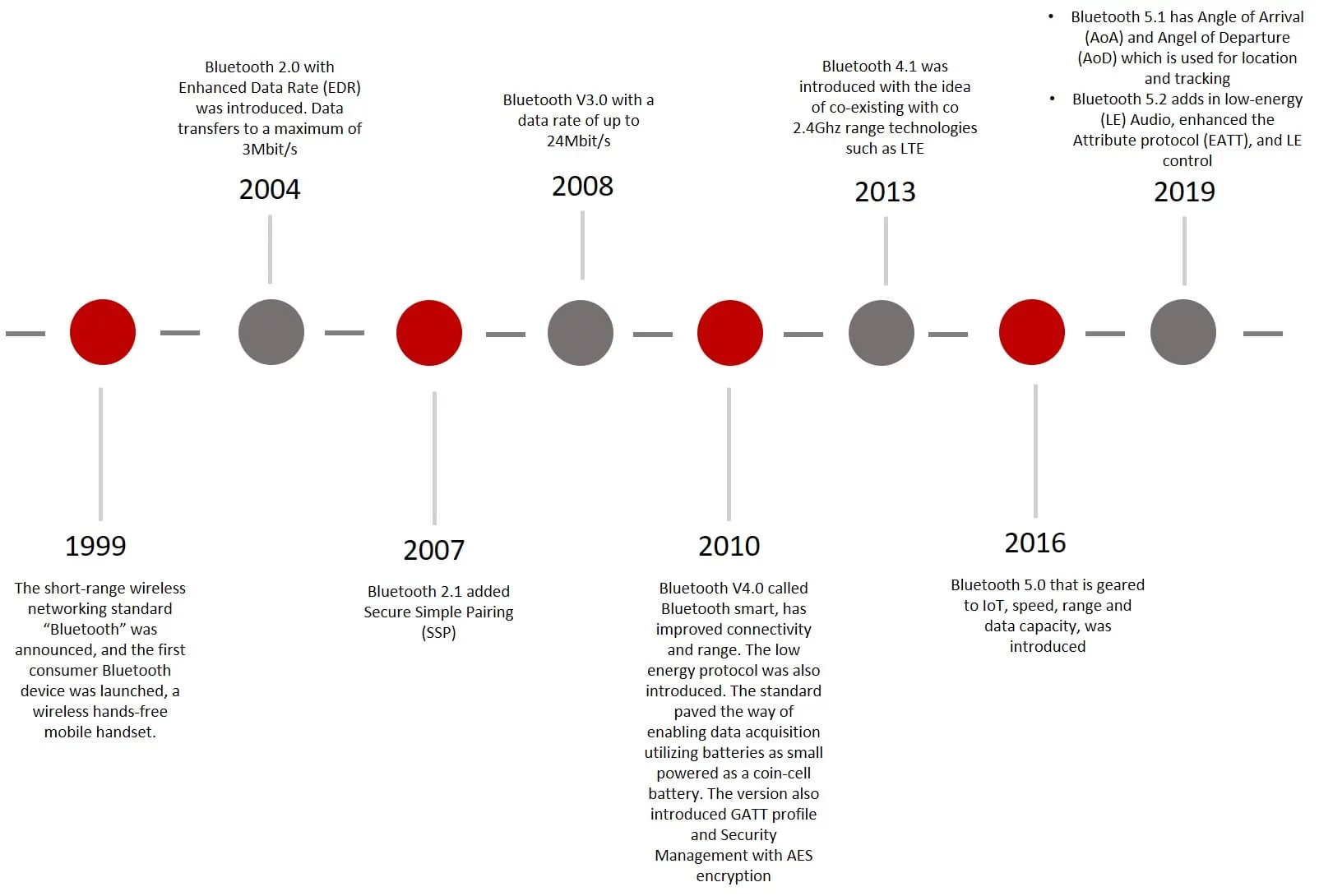 Figure 3 - 802.15.1 evolution
Figure 3 - 802.15.1 evolution
More Info…
IEEE 802.15.4 – WPAN/Zigbee/Thread (spe6LoWPAN)
The IEEE 802.15.4 standard was created to offer a low-cost, low data throughput ubiquitous communication between devices, with little to no underlying infrastructure. These wireless protocols operate in the ISM RF frequency bands (868 – 868.6 MHz in Europe, 902 – 928 MHz in North America, and the 2400 - 2483.5 MHz worldwide) since 2002.
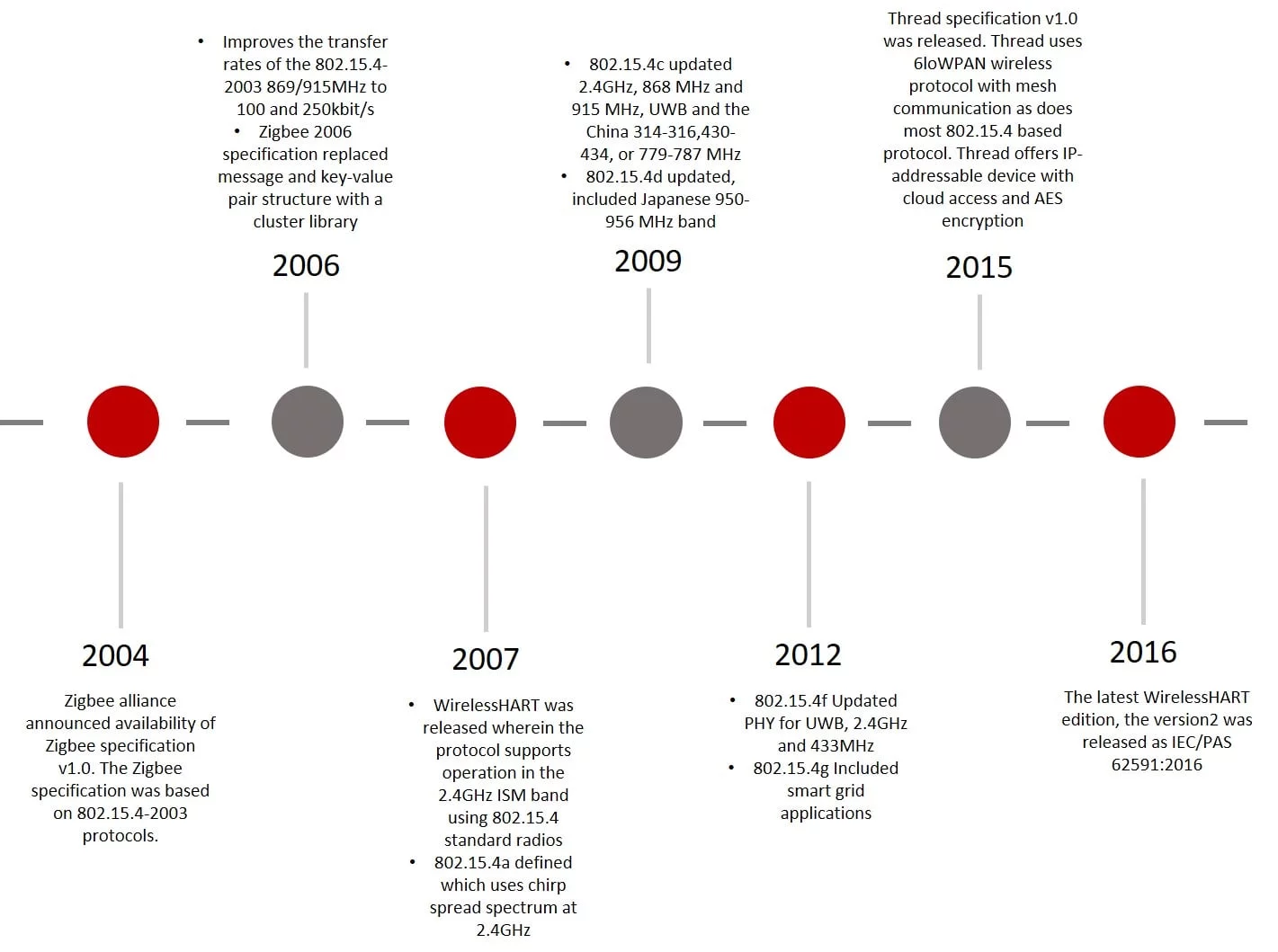 Figure 4 - 802.15.4 evolution
Figure 4 - 802.15.4 evolution
More Info…
Zigbee
Zigbee is a lower power low-rate wireless mesh networking protocol that is primarily used in battery-operated devices for wireless control and monitoring.
It came into existence in September 2006 as a specification, and is primarily used in Home Automation, Industrial control systems, smoke warning, intruder warning and building automation. It is trademark owned and maintained by the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA).
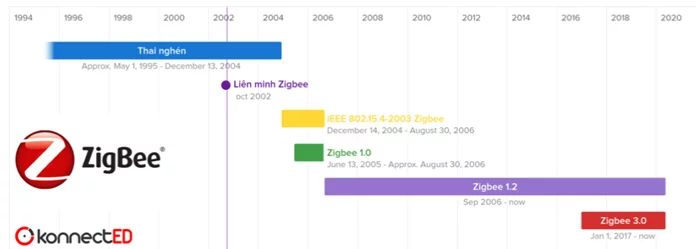 Figure 5 - Zigbee evolution
Figure 5 - Zigbee evolution
Thread
Thread is an IPv6-based low-power mesh networking protocol that uses the 802.15.4 radio technology and is specifically built for IoT devices.
Thread came into existence in 2014 when the Thread group was formed. Unlike Zigbee and Z-Wave, Thread does not need a central hub or bridges to connect and can directly talk to each other allowing for faster speed over larger networks.
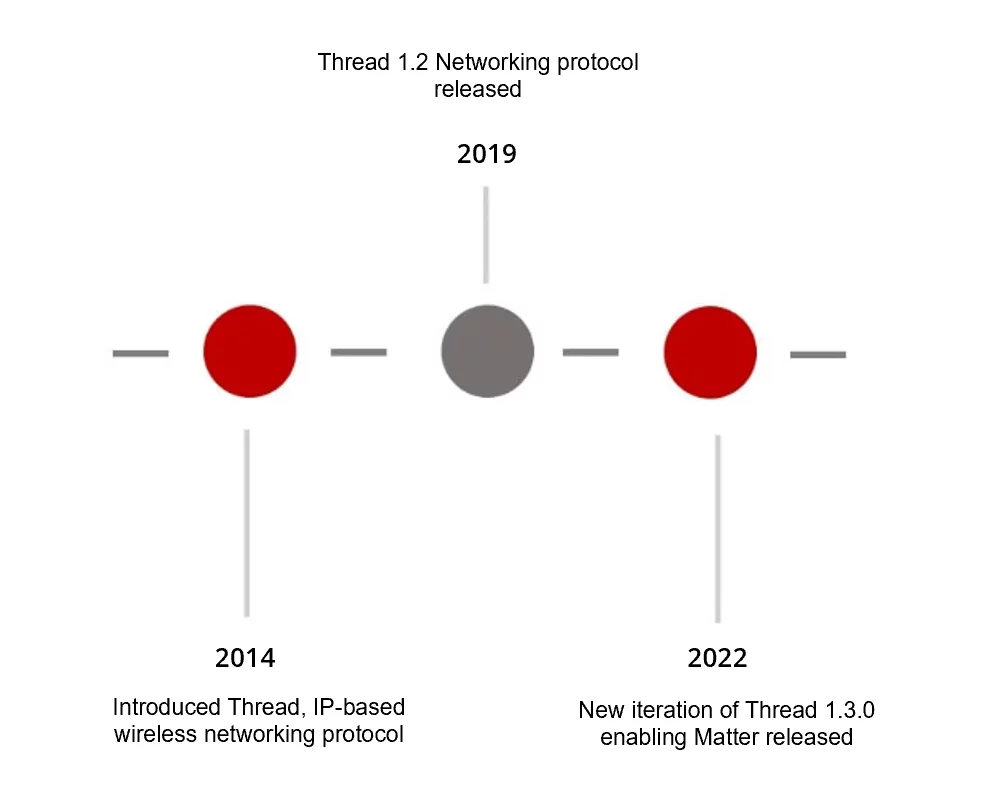 Figure 6 - Thread protocol evolution
Figure 6 - Thread protocol evolution
Cellular Data Communication Protocols
Cellular data protocols were designed to offer citywide, national and global coverage and seamless mobility from one access point to another. The various generations of wireless licensed cellular standards and protocols are developed and available via Releases by 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) as standards by the group’s worldwide organizational Partners (ARIB, ATIS, CCSA, ETSI, TSDI, TTA, TTC).
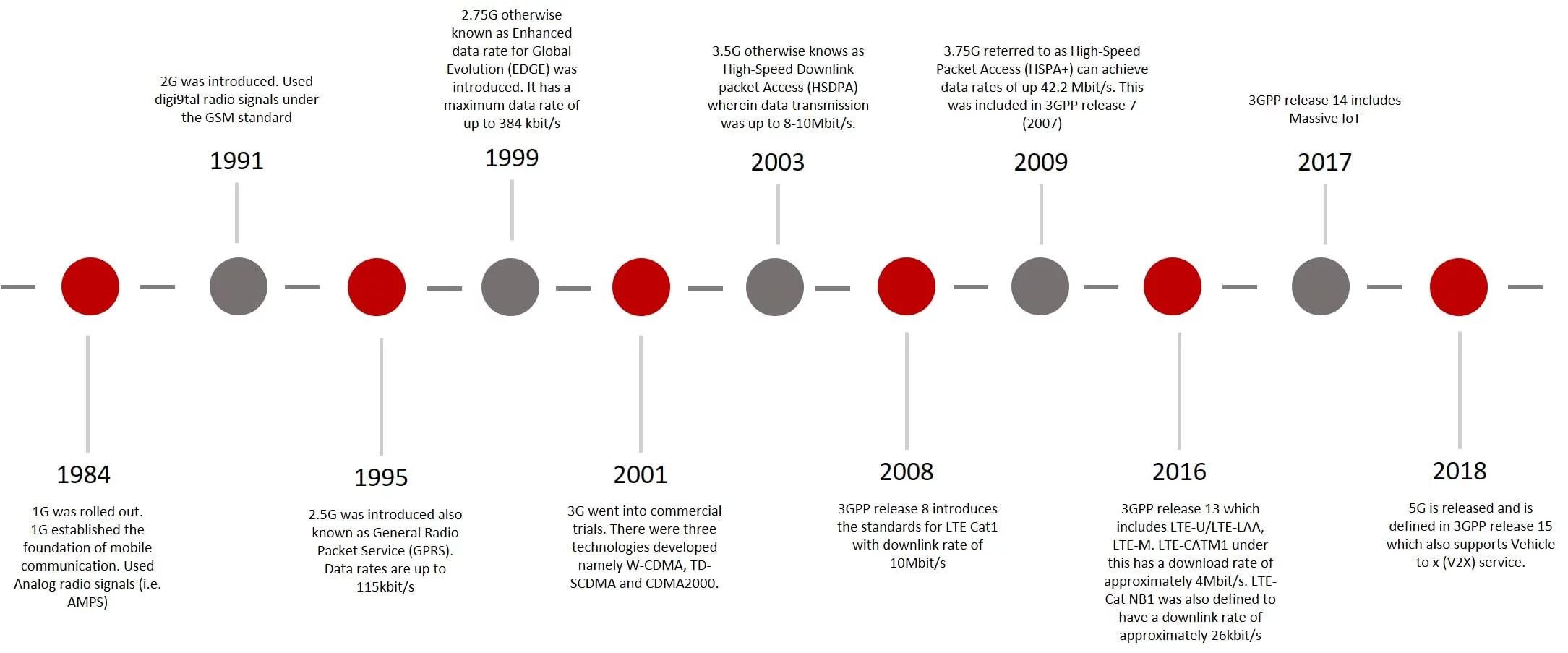 Figure 7 - Cellular data communication protocols evolution
Figure 7 - Cellular data communication protocols evolution
More Info…
LoRa
LoRa is a proprietary ITU-T Y.4480 wireless radio protocol (using spread spectrum modulation) that has revolutionized IoT by enabling data communication over a long range while using very little power. It was created for devices that need to be battery operated and last long periods of time in the field. The various specification releases are managed by the LoRa Alliance.
2009: LoRa was started under the company Cycleo. LoRa would be aimed to provide long range, low power modulation technology. RF bands includes, 434, 868, 915 and 923 MHz
2012: Semtech acquired Cycleo
2015: LoRa Alliance was formed the networking protocol and was named to LoraWAN
2018: The release of LoRaWan specification 1.03.
2020: The release of LoRaWAN specification 1.04. The additional 2.4 GHz unlicensed RF band has been introduced since Nov. 2021.
Sources – for more information please visit:
https://lora-alliance.org/sites/default/files/2018-05/2015_-_lorawan_specification_1r0_611_1.pdf
https://lora-alliance.org/sites/default/files/2018-07/lorawan1.0.3.pdf
https://blog.semtech.com/a-brief-history-of-lora-three-inventors-share-their-personal-story-at-the-things-conference.
https://iot.eetimes.com/top-wireless-standards-for-iot-devices/
Sigfox
Sigfox was created as a software-based communications solution to manage all the network and computing complexity on the Cloud, instead of on the devices, and drastically reduce energy consumption and cost of connected devices.
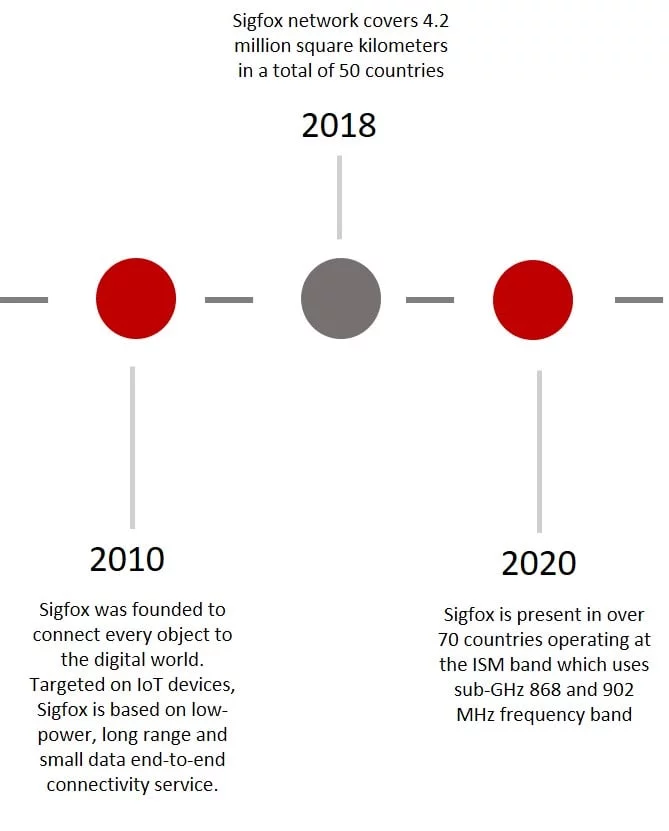 Figure 8 - Sigfox evolution
Figure 8 - Sigfox evolution
2010: Sigfox was founded to connect every object to the digital world. Targeted on IoT devices, Sigfox is based on low-power, long range and small data end-to-end connectivity service.
2018: Sigfox network covers 4.2 million square kilometers in a total of 50 countries
2020: Sigfox is present in over 70 countries operating at the ISM band which uses sub-GHz 868 and 902 MHz frequency band
Sources – for more information please visit:
https://www.sigfox.com/en/sigfox-story.
Z-Wave
Z-Wave was introduced to provide secure smart home technology that will not interfere with the Wi-Fi signal and will operate on low power. The various specification releases are managed by the Z-Wave Alliance.
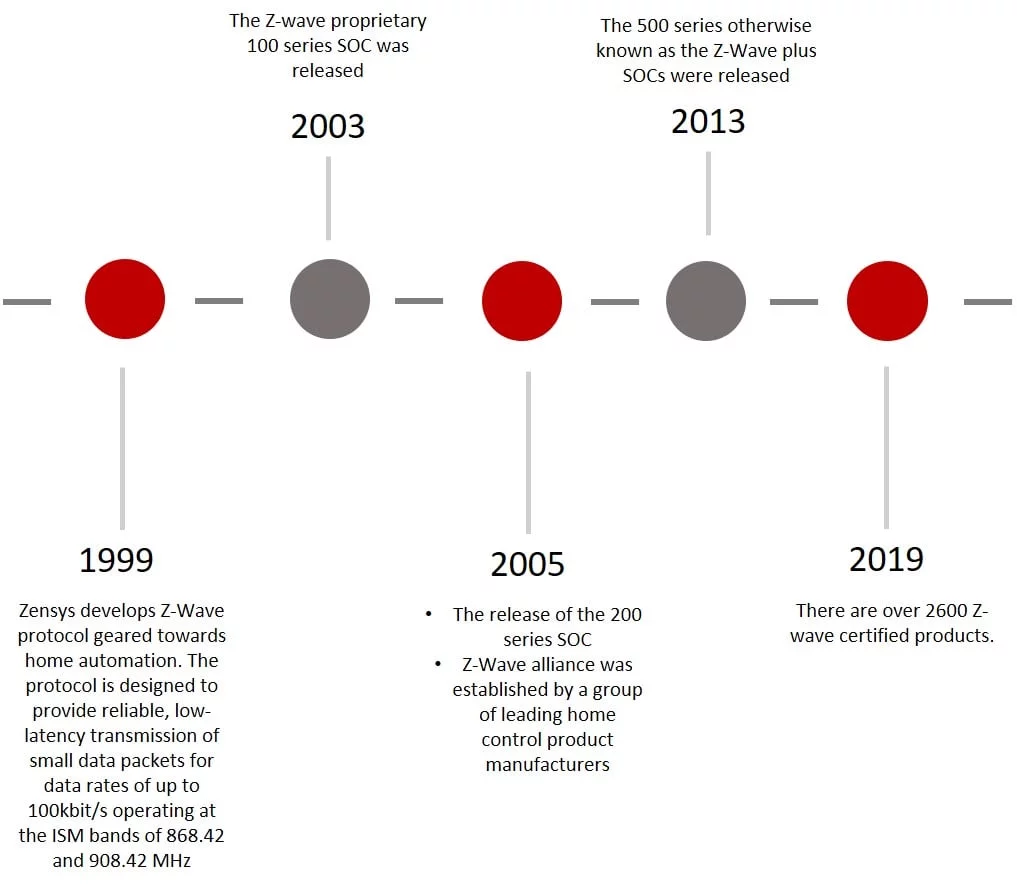 Figure 9 - Z-Wave evolution
Figure 9 - Z-Wave evolution
1999: Zensys develops Z-Wave protocol geared towards home automation. The protocol is designed to provide reliable, low-latency transmission of small data packets for data rates of up to 100kbit/s operating at the ISM bands of 868.42 and 908.42 MHz.
2003: The Z-wave proprietary 100 series SOC was released
2005: The release of the 200 series SOC
2005: Z-Wave alliance was established by a group of leading home control product manufacturers.
2008 Z-Wave was then acquired by Sigma Designs.
2013: The 500 series otherwise known as the Z-Wave plus SOCs were released
2018: Silicon Labs buys Z-wave from Sigma Designs
2019: There are over 2600 Z-wave certified products.
Sources – for more information please visit:
https://z-wavealliance.org/z-wave_alliance_history/
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Z-Wave
https://www.smarthome.com/blogs/buyers-guides/zigbee-vs-z-wave-which-is-the-best
RFID and NFC
RFID was created to identify information without a direct line of sight, be able to update information in real time.
NFC was developed for automatic wireless data collection.
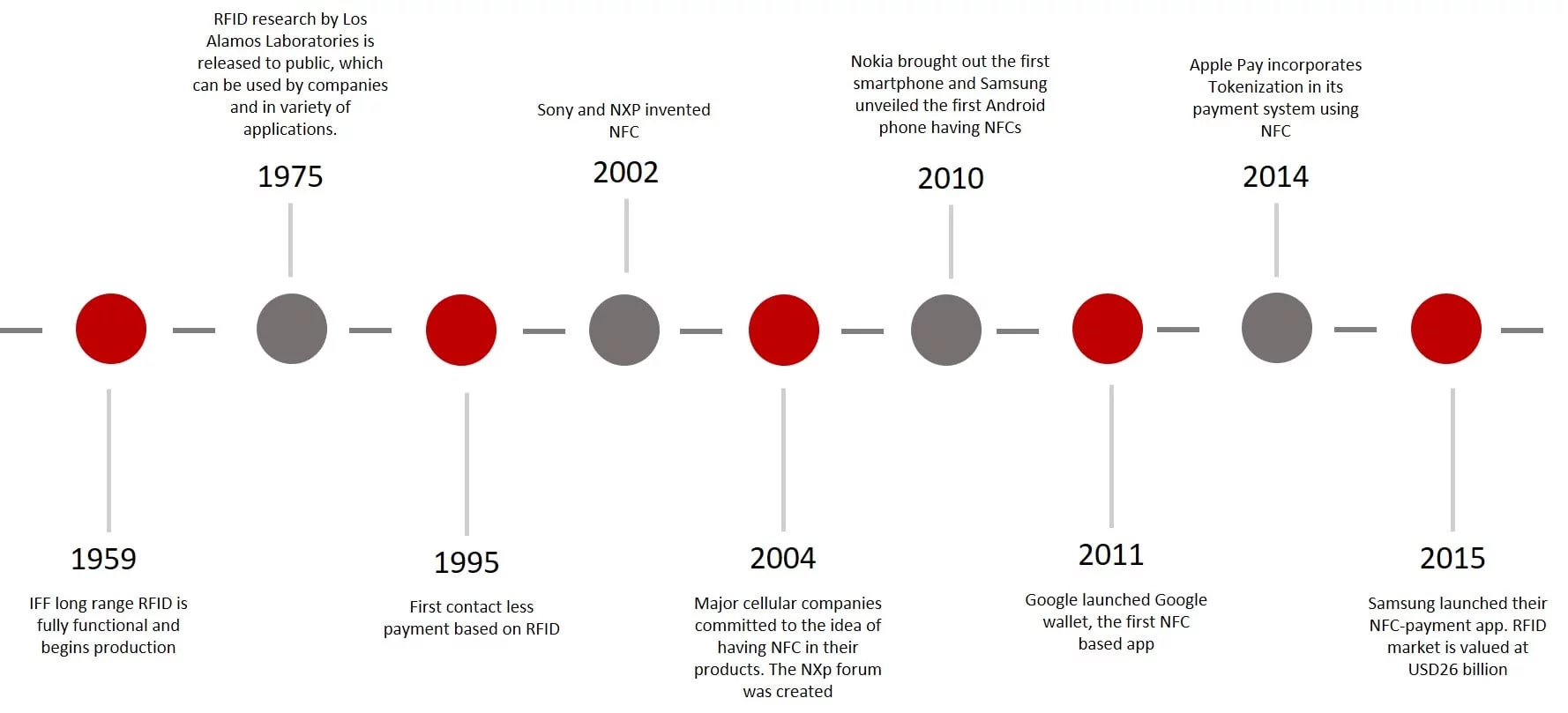 Figure 10 - RFID and NFC evolution
Figure 10 - RFID and NFC evolution
More Info…
Clearly, not all communication protocols are created equal—and with good reason. Each protocol suits certain applications. Every IoT system architecture is unique, for example. Front-end sensors have different parameters to measure. Applications have different communication methodologies and different data payload formats that need to be followed. It’s no wonder, then, that we need to consider the feasibility of what communication protocol to implement for each project.
Our historical timeline of wireless technologies will help give you a consumer-side overview of the stability, support, and security you should expect from each standard based on what industry each protocol will be implemented into.
2. Wireless Communication Protocol Comparison Table
Each wireless communication protocol has its own pace of evolution—some took 50 years to evolve, some are still in their infancy and just getting traction. So, while we’ve seen how each protocol evolved, how does each compare? How are they similar or dissimilar in their data rate, range, topologies, or cost, to name a few?
As a Systems Engineer, at the onset of a project you need to consider the technologies you plan on using and evaluate how will they perform based on the specifications of the project. The table below offers some guidelines for comparison on how the various protocols can be implemented.
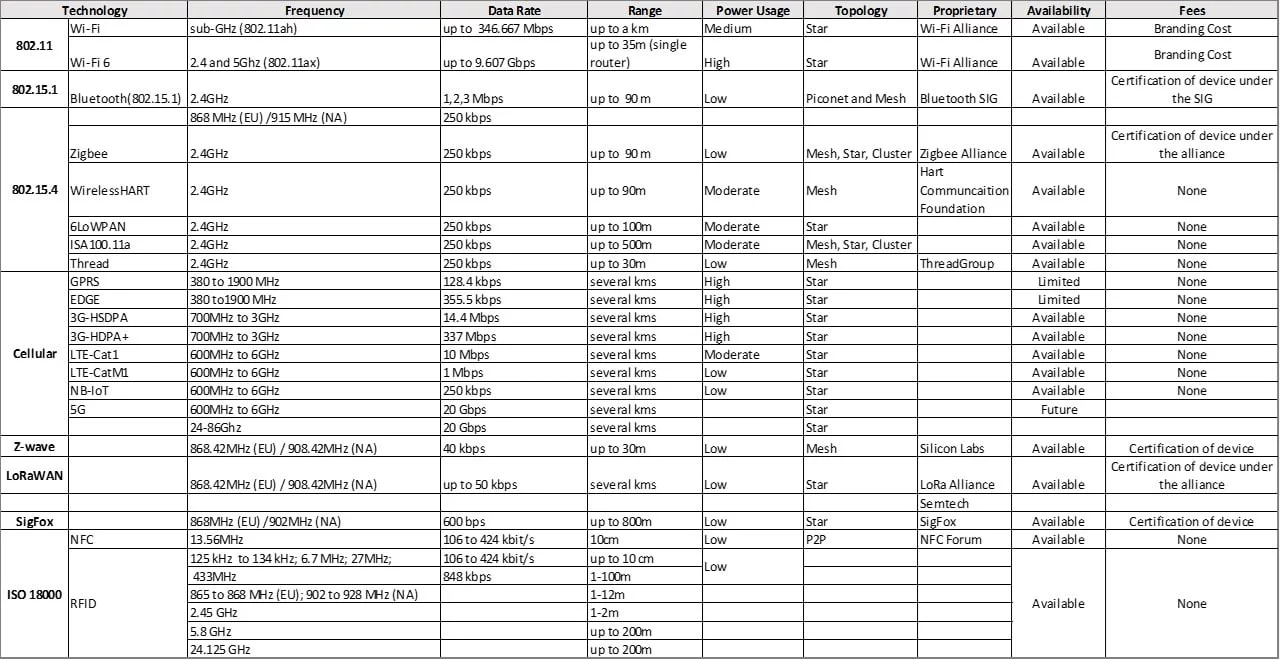 Table 1 – Wireless Communication Protocol Comparison Table
Table 1 – Wireless Communication Protocol Comparison Table
Sources – for more information please visit:
https://www.postscapes.com/internet-of-things-protocols/
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325706554_Trends_and_Issues_in_5G_Networking_and_Beyond/figures?lo=1
You can see from this table some points of similarity and divergence between the various protocols.
Applications that need high data rate—video, for example—can use Wi-Fi or 4G LTE-Cat1. Sub-systems utilizing LoRaWAN might need a gateway to have data be sent to a back-end cloud system.
Your considerations should also cover the power needs of each node. For a system that is low-data and low power, options like LoRaWAN, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) 5.0, 4G LTE-Cat M1, Cat-NB-IoT would be appropriate.
And what should also be clear from the table are the considerations that go in to deploying each protocol, including:
• Frequency of operation
• Deployment topology
• Support for the technologies (from industry alliances)
On a use-case perspective, keep in mind how technicians or engineers will be interacting with the edge devices. What specific in-field device will they likely be using? An Android tablet or phone? A Window-OS based device? The availability of 4G LTE or 5G NR FR1 cellular cannot be implemented without a cell signal—will that factor in to use cases? Do you need to rethink your design if deployment will be in a dense mobile data user area?
3. Performance Chart
For quick reference, below you’ll find a visualization of the performance of the various communication protocols. We wanted to offer something from the perspective of our clients that provides a visual cross-referencing of the range, data rate, and power consumption of the wireless communication protocols covered in the more extensive chart above.
The graphic below superimposes the capabilities of each protocol for easy reference at a glance.
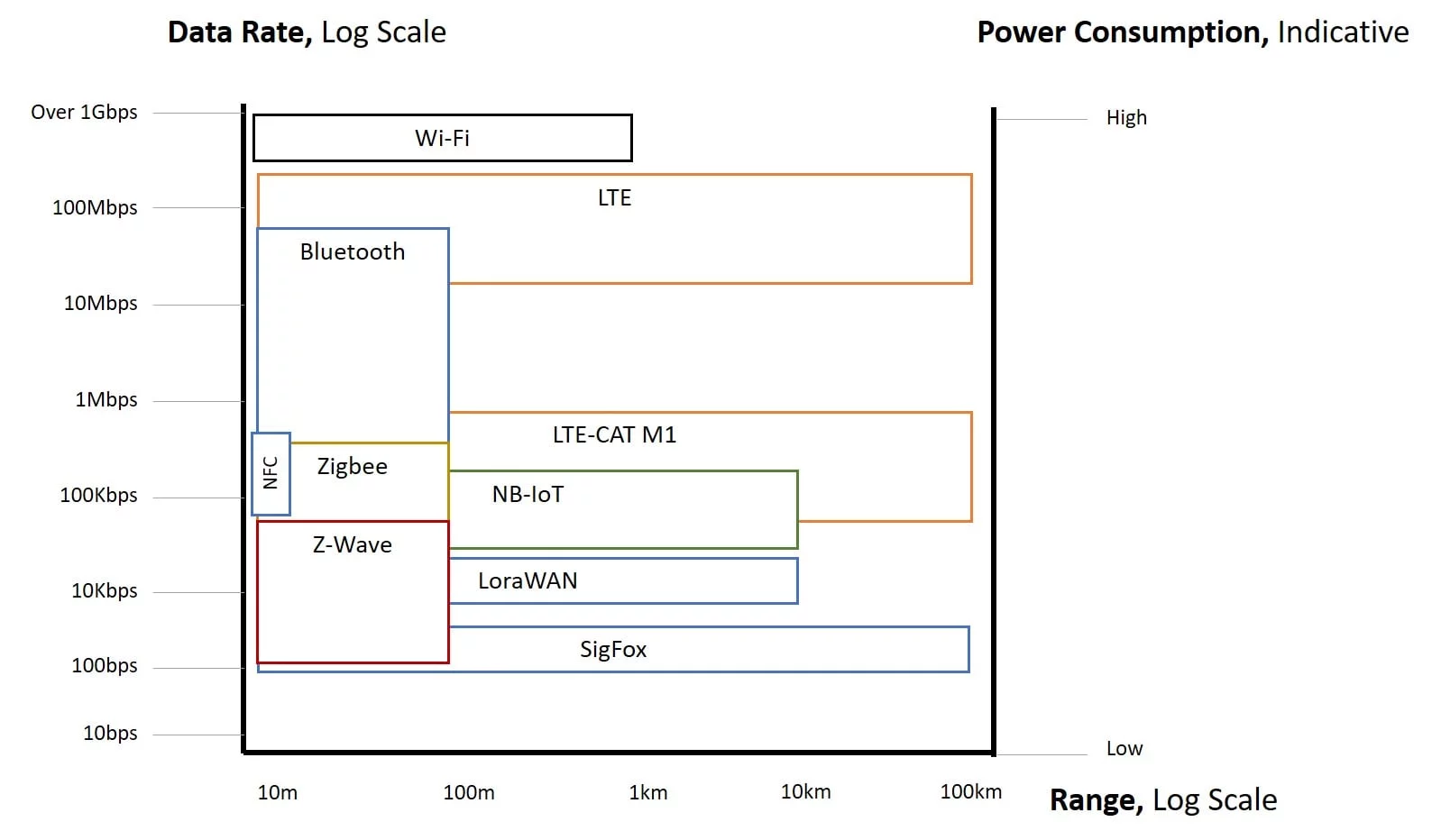 Figure 11 – Performance Chart
Figure 11 – Performance Chart
As you can see from the Figure 11 above, there are clear areas of overlap between the various standards, as well as areas where one might perform better than another.
In terms of range, Sigfox, LoRa and 4G LTE leads the pack. However, highly urbanized areas provide numerous signal obstructions, reducing the effective range for each in real-world implementations. 4G and LTE use cellular networks, so the density or volume of devices in a single cell network needs to be factored in when considering those protocols.
For home automation, a standard home set-up means each node must effectively communicate with a router or a hub in a star network configuration. Thus, Zigbee or even Z-wave is the most suitable for this application. In an industrial setup, however, an option to extend range to implement mesh topology, or have an extended star network configuration is important. Not to be outdone, for M2M communication applications up to 10cm, NFC is the strongest choice.
When considering data rate, IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) and 4G LTE cellular wireless communication provides more room to send information, including applications like real-time monitoring of industrial systems or video applications. Moderate data rates suit IEEE 802.11ah (HaLow) (uses sub 1GHz license exempt frequency bands), Zigbee, Thread, Z-wave, and NFC, while low data rates favor Sigfox.
Likewise, looking at power consumption shows us that Wi-Fi needs more power to function, but keep in mind that IEEE 802.11ah is a promising alternative and is disrupting this mind set. Sigfox and LoRaWAN are most useful in low-power consumption applications.
4. New communication protocols
Wireless communication may have been ushered in by Marconi 125 years ago, but its evolution is far from over. While we’ve discussed a number of well-established, standardized wireless communication protocols, the formats continue to evolve and innovators continue to develop new languages to help wireless communication develop well into the 21st Century.
Already the 802.11 standard —and the high data rate it provides—has become something of a ‘household name’ for residential and commercial uses. 802.15.4 and the LR-WPAN protocols provide an avenue to connect industrial measurements and controls, as well as applications in home automation. 802.15.1 provides a means of peer-to-peer (P2P) connectivity. And 802.15.4w LPWAN transmits power to the order of 10mW, while achieving long-range communication of up to 15km in rural areas and would also penetrate buildings in an urban area.
New wireless communication protocols continue to debut and the last few years have witnessed innovations like MIOTY protocol (Behr), Low power Wi-Fi (InnoPhase), Sigfox, MulteFire (based on 3GPP LTE Releases 13 & 14 for co-existence with Wi-Fi in the 5 GHZ frequency band), and 5G NR FR1 that have gained traction in the market.
Recently, the Connectivity Standards Alliance (CSA) released the Matter protocol, supported by manufacturers of Home Automation SoCs and Modules, that will bridge the LPWAN wireless communications protocols (Zigbee, Z-Wave) to network IP-based wireless communications protocols (THREAD, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth).
Matter protocol is a huge step forward for smart home technology allowing devices to work together regardless of protocols. The potential is huge and it will be exciting to see what the future holds for us in the area of home automation.
To be informed when these and other articles become available, join our mailing list now to gain access to our exclusive monthly newsletter.